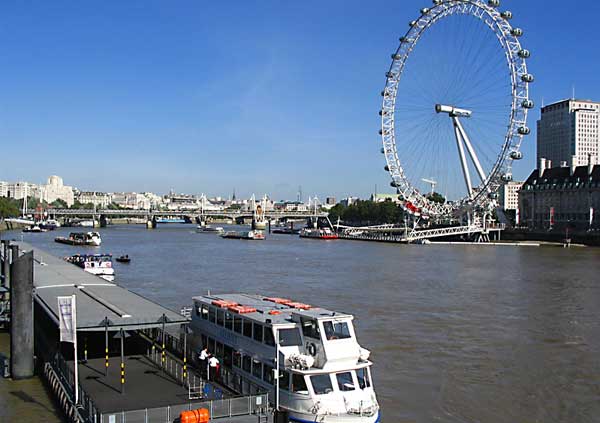
The River Thames (/tɛmz/ (About this sound listen) TEMZ) is a river that flows through southern England, most notably through London. At 215 miles (346 km), it is the longest river entirely in England and the second longest in the United Kingdom, after the River Severn. It also flows through Oxford (where it is called Isis), Reading, Henley-on-Thames and Windsor. The lower reaches of the river are called the Tideway, derived from its long tidal reach up to Teddington Lock. It rises at Thames Head in Gloucestershire, and flows into the North Sea via the Thames Estuary. The Thames drains the whole of Greater London.
Its tidal section, reaching up to Teddington Lock, includes most of its London stretch and has a rise and fall of 7 metres (23 ft). Running through some of the driest parts of mainland Britain and heavily abstracted for drinking water, the Thames' discharge is low considering its length and breadth: the Severn has a discharge almost twice as large on average despite having a smaller drainage basin. In Scotland, the Tay achieves more than double the average discharge from a drainage basin that is 60% smaller.
Along its course are 45 navigation locks with accompanying weirs. Its catchment area covers a large part of South Eastern and a small part of Western England and the river is fed by 38 named tributaries.[citation needed] The river contains over 80 islands. With its waters varying from freshwater to almost seawater, the Thames supports a variety of wildlife and has a number of adjoining Sites of Special Scientific Interest, with the largest being in the remaining parts of the North Kent Marshes and covering 5,449 hectares (13,460 acres).
In 2010, the Thames won the largest environmental award in the world – the $350,000 International Riverprize.