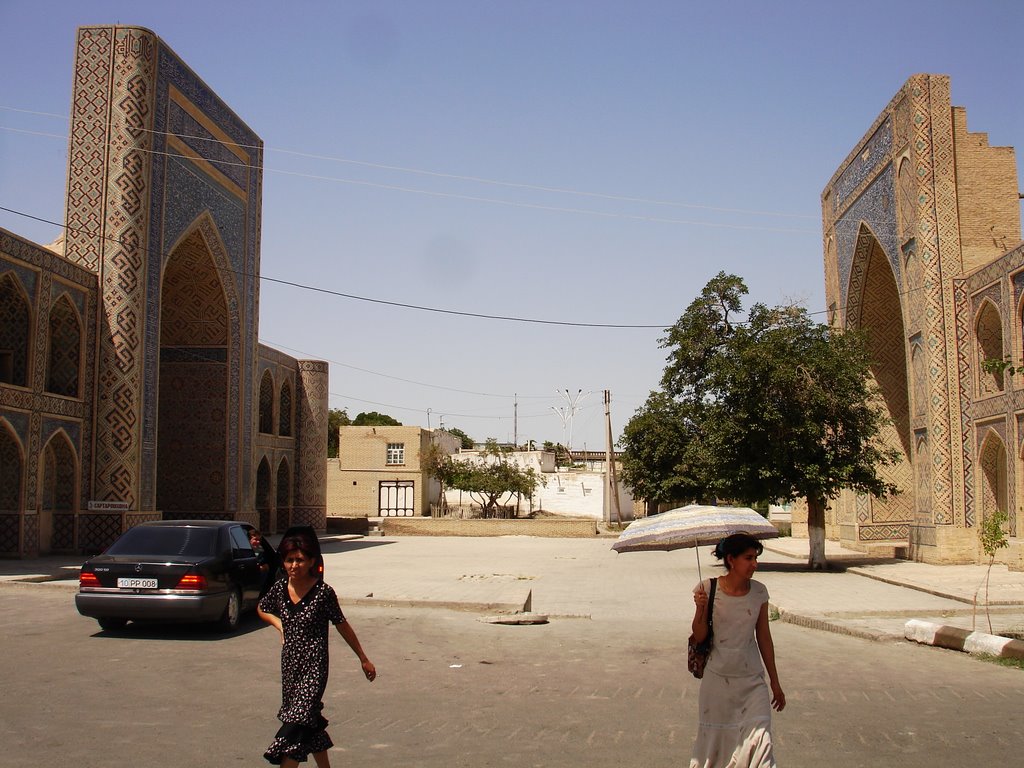
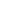
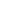
In the same district with the Samanid mausoleum and Chashma-iy-Ayub, not far from the park is situated one of the most interesting ensembles of Bukhara "Kosh-Madrasah" (Kosh Madrasah Ensemble), which is typical of Bukhara. The word "Kosh" means "paired" because two structures of the ensemble face one another across a narrow street.
Modari-Khan Madrassah (1567)
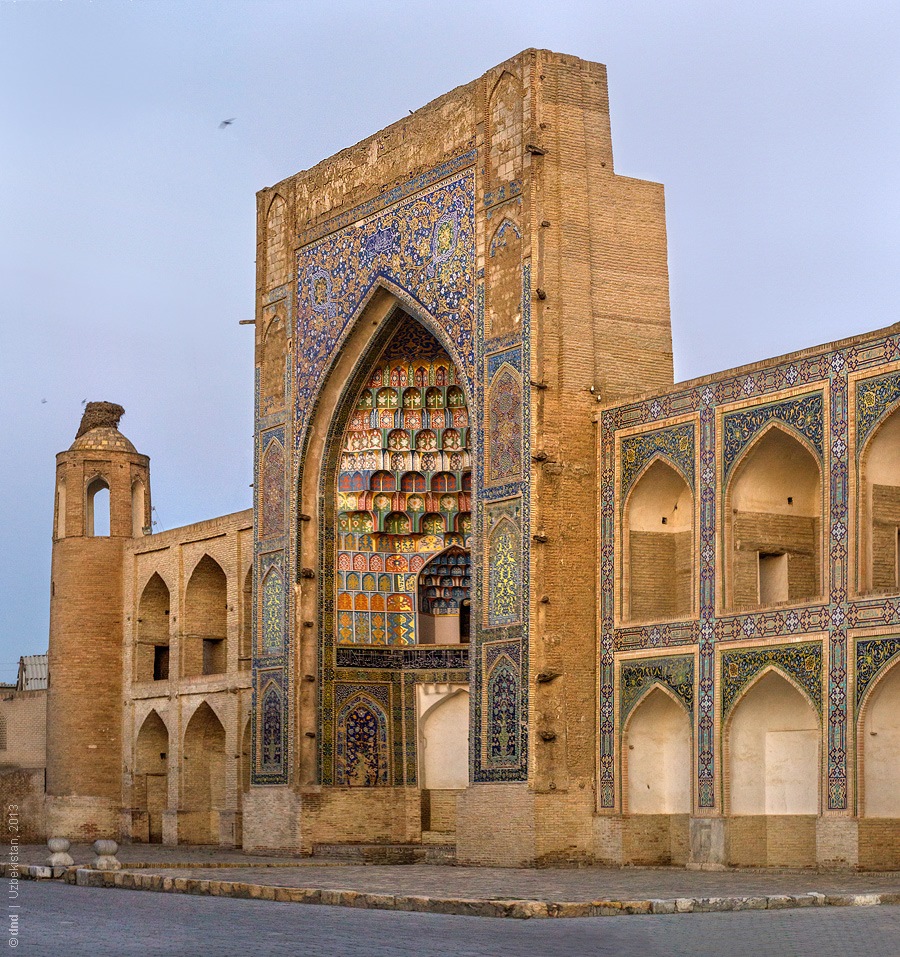
The sponsor of the Ensemble was Abdullah-khan II (1561-1598), the most successful khan of Shaibanid dynasty. In 974 A.H. (1566-67) he built up the Modari-khan Madrasahin memory of his mother (“Modari-khan” means “mother of khan”). The date of construction is inserted in majolica inscription above the main entrance. As to composition of structure, the madrasah has fairly standard layout including a dormitory, which consists of small cells (hudjras) around a courtyard, public halls of a mosque and lecture-rooms (darskhana)along both sides of front. The facade (peshtaq) of the madrasah has gorgeous appearance because of multicolor brick mosaic.
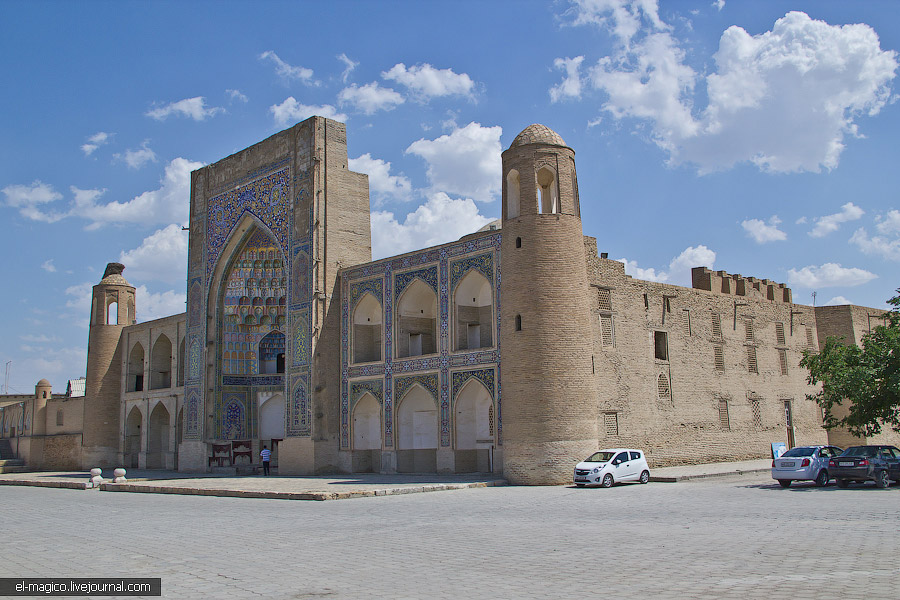
Abdullah-khan Madrassah (1588-1590)
Date of construction of the Abdullah-khan Madrasahis between 1588-90 years. The madrasah has very colorful and festive look because of variety of decorative methods. Chilled colors of majolica slabs: blue, white and aquamarine are sparkling by the sunlight.
Unlike some madrasahs with blind wings of their fronts, the facades of the Modari-khan Madrasah and the Abdullah-khan Madrasah have arched doorways to the lecture-rooms from the street on ground floor and from loggias on second floor. The Abdullah-khan Madrasah is one of three greatest madrasahs in Bukhara after Kukeldashand Mir-i Arab.
Architecturally, Abdullah-khan Madrassah is more complex than Madrassah of Modari-khan. The entrance hall forms a gallery with two passages to the court yard. Mosque and classrooms (darskhana) are located in the gallery.
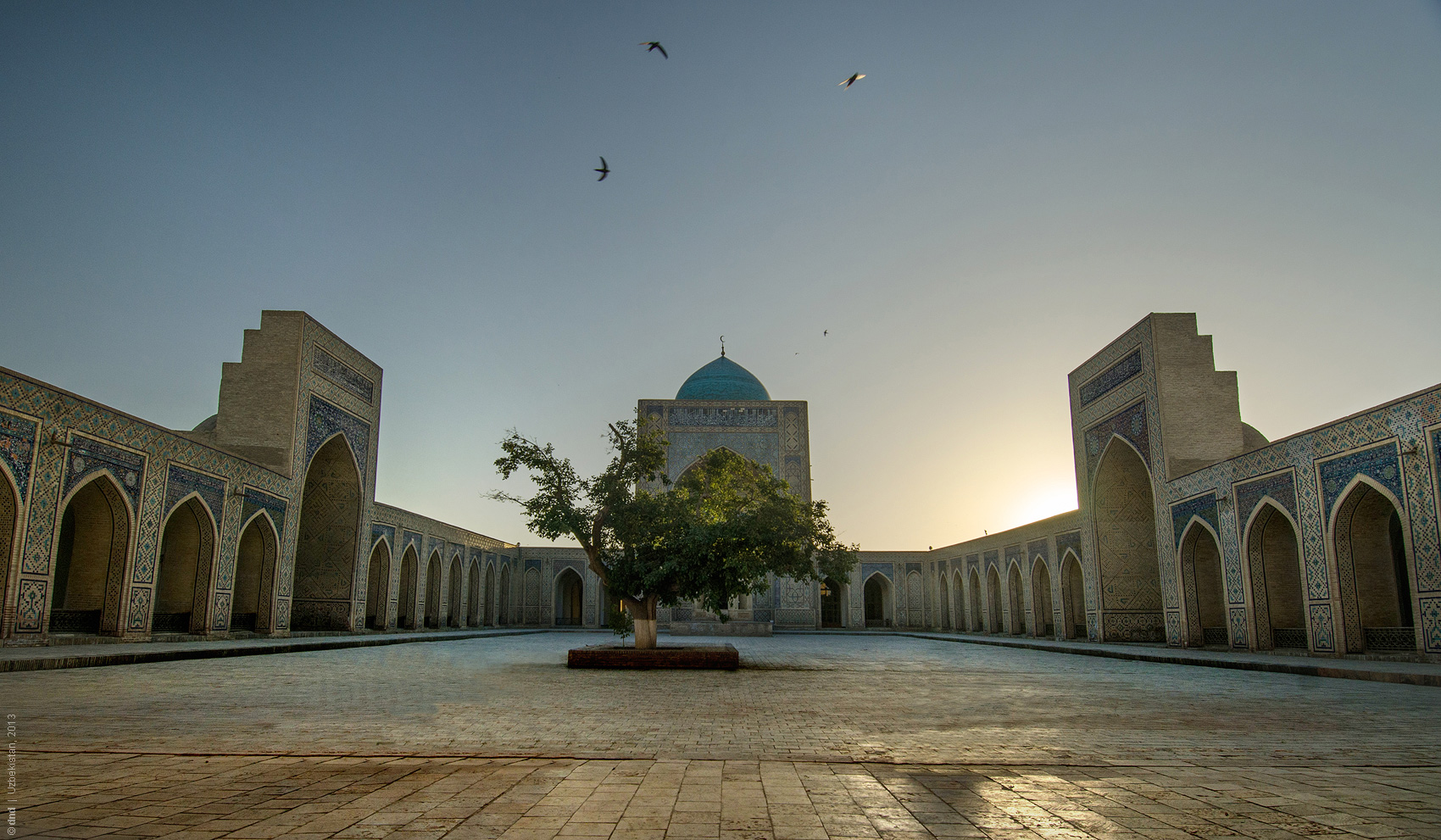
The mosque is located at angle with major building. It was done to focus a praying niche (mihrab) right to Mecca. The inner courtyard has four aivans with high portals.
Majolica was used instead of polychromic mosaic for facing. Geometrical patterns of five, eight and nine-point stars originally decorated the dome.