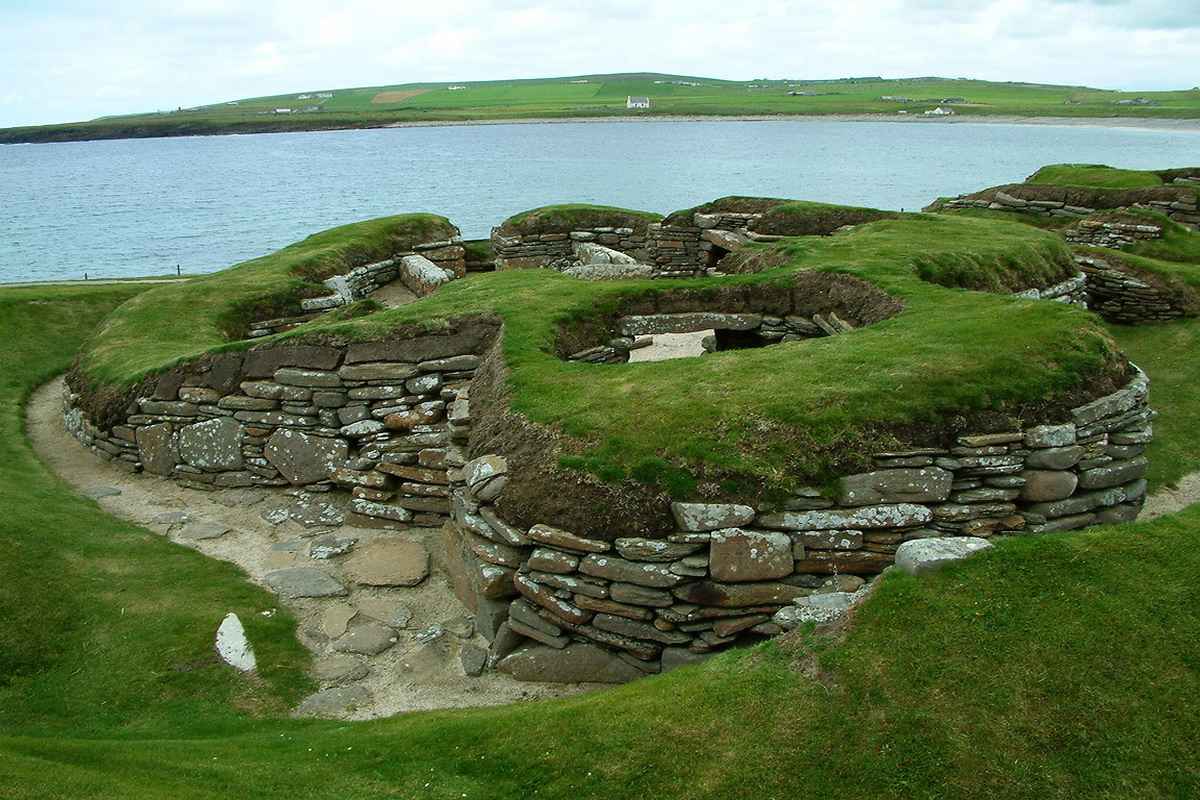
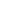
Skara Brae is a stone-built Neolithic settlement, located on the Bay of Skaill on the west coast of Mainland, the largest island in the Orkney archipelago of Scotland. It consists of eight clustered houses, and was occupied from roughly 3180 BCE–2500 BCE. Europe's most complete Neolithic village, Skara Brae gained UNESCO World Heritage Site status as one of four sites making up "The Heart of Neolithic Orkney."a Older than Stonehenge and the Great Pyramids, it has been called the "Scottish Pompeii" because of its excellent preservation.
In the winter of 1850, a severe storm hit Scotland, causing widespread damage and over 200 deaths. In the Bay of Skaill, the storm stripped the earth from a large irregular knoll known as "Skerrabra". When the storm cleared, local villagers found the outline of a village, consisting of a number of small houses without roofs. William Watt of Skaill, the local laird, began an amateur excavation of the site, but after four houses were uncovered, the work was abandoned in 1868. The site remained undisturbed until 1913, when during a single weekend the site was plundered by a party with shovels who took away an unknown quantity of artefacts. In 1924, another storm swept away part of one of the houses and it was determined the site should be made secure and more seriously investigated. The job was given to University of Edinburgh's Professor Vere Gordon Childe who travelled to Skara Brae for the first time in mid-1927.
Skara Brae
- Continent: Europe
- Country: United Kingdom
- Category: Other
- Added by: Mirtoirova Malika Mirodil qizi
- Source: https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%A1%D0%BA%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%
- Date of adding: 2015-12-15 17:38:56
- 0
- 0
Description
Расположение на карте
Comments