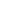
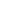
Harlech Castle, located in Harlech, Gwynedd, Wales, is a medieval fortification, constructed atop a spur of rock close to the Irish Sea. It was built by Edward I during his invasion of Wales between 1282 and 1289 at the substantial cost of £8,190. Over the next few centuries, the castle played an important part in several wars, withstanding the siege of Madog ap Llywelyn between 1294–95, but falling to Owain Glyndŵr in 1404. It then became Glyndŵr's residence and military headquarters for the remainder of the uprising until being recaptured by English forces in 1409. During the 15th century Wars of the Roses, Harlech was held by the Lancastrians for seven years, before Yorkist troops forced its surrender in 1468, a siege memorialised in the song Men of Harlech. Following the outbreak of the English Civil War in 1642, the castle was held by forces loyal to Charles I, holding out until 1647 when it became the last fortification to surrender to the Parliamentary armies. In the 21st century the ruined castle is managed by Cadw, the Welsh Government's historic environment service, as a tourist attraction.
UNESCO considers Harlech to be one of "the finest examples of late 13th century and early 14th century military architecture in Europe", and it is classed as a World Heritage site. The fortification is built of local stone and concentric in design, featuring a massive gatehouse that probably once provided high-status accommodation for the castle constable and visiting dignitaries. The sea originally came much closer to Harlech than in modern times, and a water-gate and a long flight of steps leads down from the castle to the former shore, which allowed the castle to be resupplied by sea during sieges. In keeping with Edward's other castles in North Wales, the architecture of Harlech has close to links to that found in the kingdom of Savoy during the same period, an influence probably derived from the Savoy origins of the main architect, James of Saint George.
History
13th–14th centuries
In local mythology, the site of Harlech Castle in North Wales is associated with the legend of Branwen, a Welsh princess, but there is no evidence for a native Welsh fortification having been built there. The kings of England and the Welsh princes had vied for control of North Wales since the 1070s and the conflict was renewed during the 13th century, leading to Edward I intervening in North Wales for the second time during his reign in 1282. Edward invaded with a huge army, pushing north from Carmarthen and westwards from Montgomery and Chester. English forces advanced down the Conwy valley and through Dolwyddelan and Castell y Bere, onto Harlech, which Sir Otton de Grandson took with 560 infantry in May.
Edward ordered the construction of a castle at Harlech, one of seven built across North Wales in the wake of the 1282 campaign. Money to pay for the initial phase arrived in mid-May and carpenters and 35 stonemasons were dispatched in June and July to commence work. By the winter of 1283, the first 15 feet (4.6 m) of the inner walls had been constructed, allowing the castle to be defended in the event of an attack, and a small, planned town had been founded alongside the castle. Sir John Bonvillars was appointed the constable of the castle in 1285; after his death in 1287 his wife, Agnes, took up the role until 1290.
Construction continued under the overall direction of James of Saint George, a Savoy architect and military engineer. In 1286, at the height of the construction, the workforce comprised 546 general labourers, 115 quarriers, 30 blacksmiths, 22 carpenters and 227 stonemasons, and the project was costing nearly £240 a month. The castle was essentially complete by the end of 1289, having cost an estimated £8,190, around 10 percent of the £80,000 that Edward spent on castle-building in Wales between 1277 and 1304.
Harlech was established with a garrison of 36 men: a constable, 30 men, including 10 crossbowmen, a chaplain, a smith, carpenter and stonemason, and Master James was rewarded by being made the constable of Harlech from 1290–93. In 1294, Madog ap Llywelyn began an uprising against English rule that spread quickly through Wales. Several English-held towns were razed and Harlech, along with Criccieth Castle and Aberystwyth Castle, were besieged that winter. Fresh supplies were sent from Ireland by sea, arriving via Harlech's water gate, and the uprising was quashed. In the aftermath of the revolt, additional defences were built around the route down to the sea. Further work was undertaken between 1323–24, following the Despenser War; Edward II was threatened in the region by the Mortimer Marcher Lord family, and ordered his sheriff, Sir Gruffuld Llywd, to extend the defences leading up to the gatehouse with additional towers.
18th–21st centuries
In the late-18th and 19th centuries, the picturesque ruins of Harlech began to attract visits from prominent artists, including John Cotman, Henry Gastineau, Paul Sandby, J. M. W. Turner and John Varley. In 1914 it was transferred from the Merioneth Crown Estate to the control of the Office of Works, who commenced a major restoration project after the end of World War I. In 1969 the castle was transferred to the Welsh Office and then to Cadw, who manage the property in the 21st century as a tourist attraction. Harlech was declared part of the Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd World Heritage site in 1986, UNESCO considering Harlech one of "the finest examples of late 13th century and early 14th century military architecture in Europe".